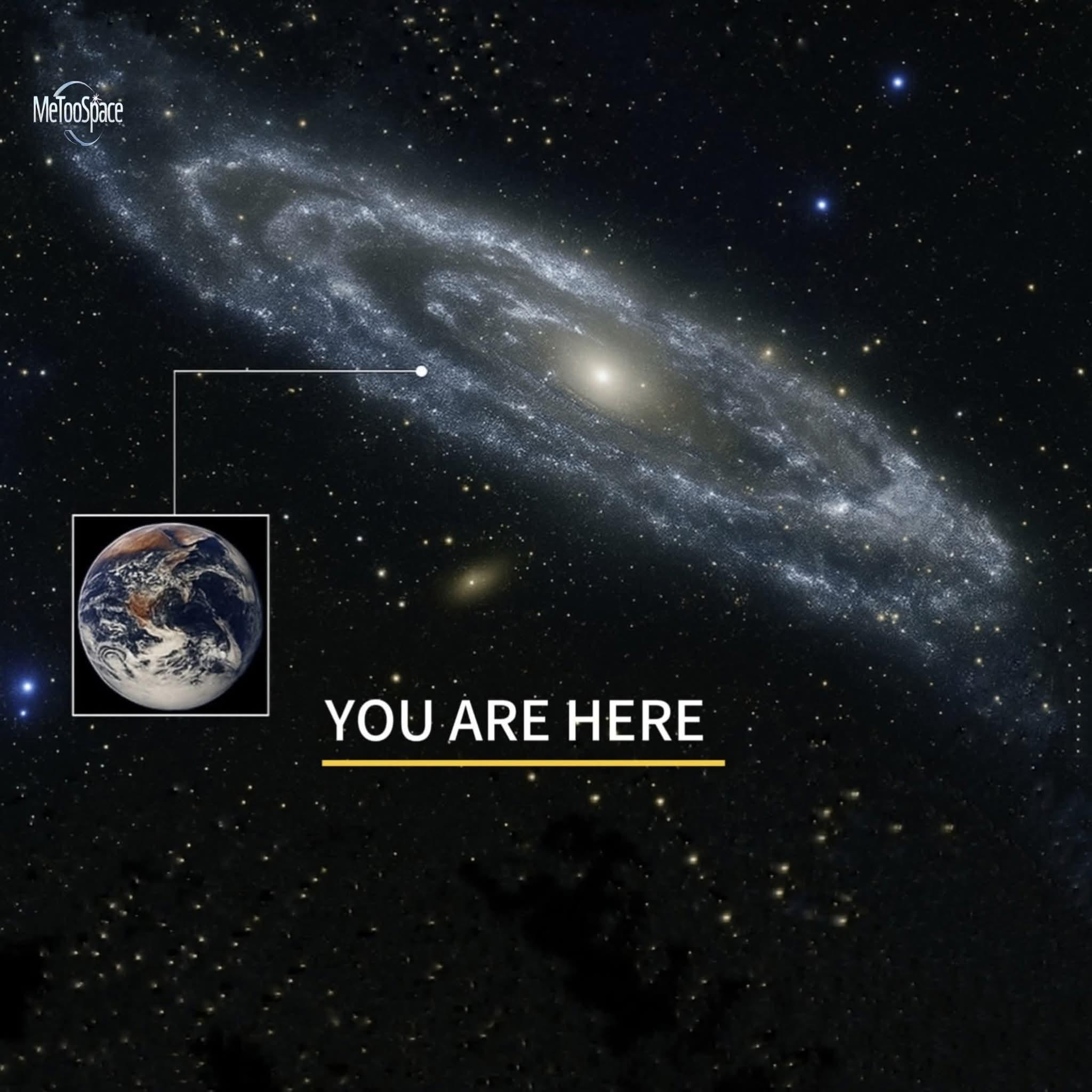
We humans live in a strange paradox — the majority of reality is hidden from us.
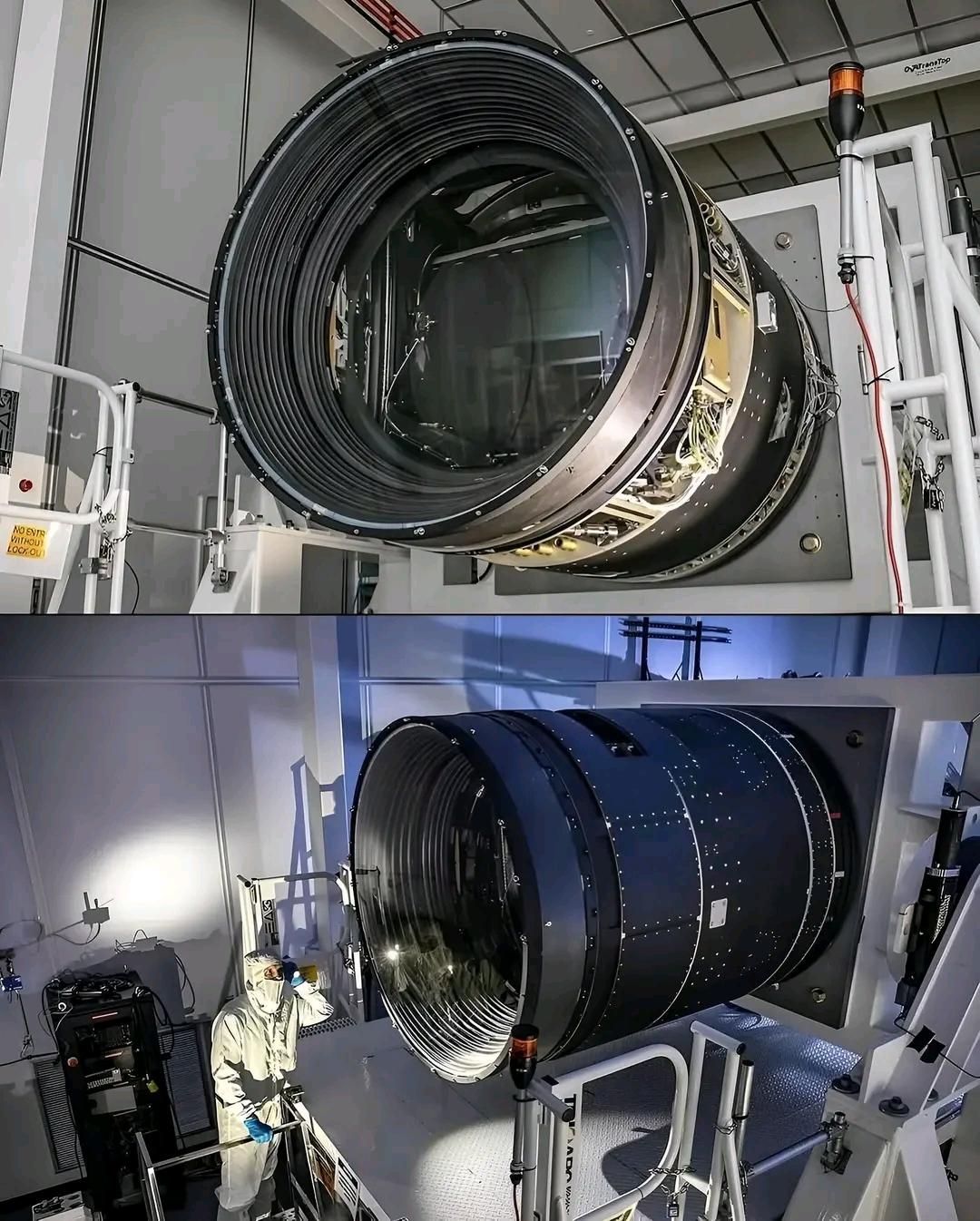
Astronomers estimate that about 95% of the universe is made up of mysterious dark matter and dark energy, invisible to the naked eye and detectable only through advanced science.
But the unseen isn’t just “out there” in space — it’s all around us. Our senses are tuned to a very small slice of reality: a narrow spectrum of light, a limited range of sounds. Beyond those limits exist ultraviolet rays, radio waves, infrasound, and countless other signals shaping the world in ways we rarely notice.
From deep-ocean animal calls to ghostlike particles streaming through our bodies, modern tools are only beginning to reveal the hidden layers of existence. It makes you wonder how much of reality is still waiting to be uncovered?
Astronomers estimate that about 95% of the universe is made up of mysterious dark matter and dark energy, invisible to the naked eye and detectable only through advanced science.
But the unseen isn’t just “out there” in space — it’s all around us. Our senses are tuned to a very small slice of reality: a narrow spectrum of light, a limited range of sounds. Beyond those limits exist ultraviolet rays, radio waves, infrasound, and countless other signals shaping the world in ways we rarely notice.
From deep-ocean animal calls to ghostlike particles streaming through our bodies, modern tools are only beginning to reveal the hidden layers of existence. It makes you wonder how much of reality is still waiting to be uncovered?
We humans live in a strange paradox — the majority of reality is hidden from us.
Astronomers estimate that about 95% of the universe is made up of mysterious dark matter and dark energy, invisible to the naked eye and detectable only through advanced science.
But the unseen isn’t just “out there” in space — it’s all around us. Our senses are tuned to a very small slice of reality: a narrow spectrum of light, a limited range of sounds. Beyond those limits exist ultraviolet rays, radio waves, infrasound, and countless other signals shaping the world in ways we rarely notice.
From deep-ocean animal calls to ghostlike particles streaming through our bodies, modern tools are only beginning to reveal the hidden layers of existence. It makes you wonder how much of reality is still waiting to be uncovered?
0 Comments
0 Shares
609 Views