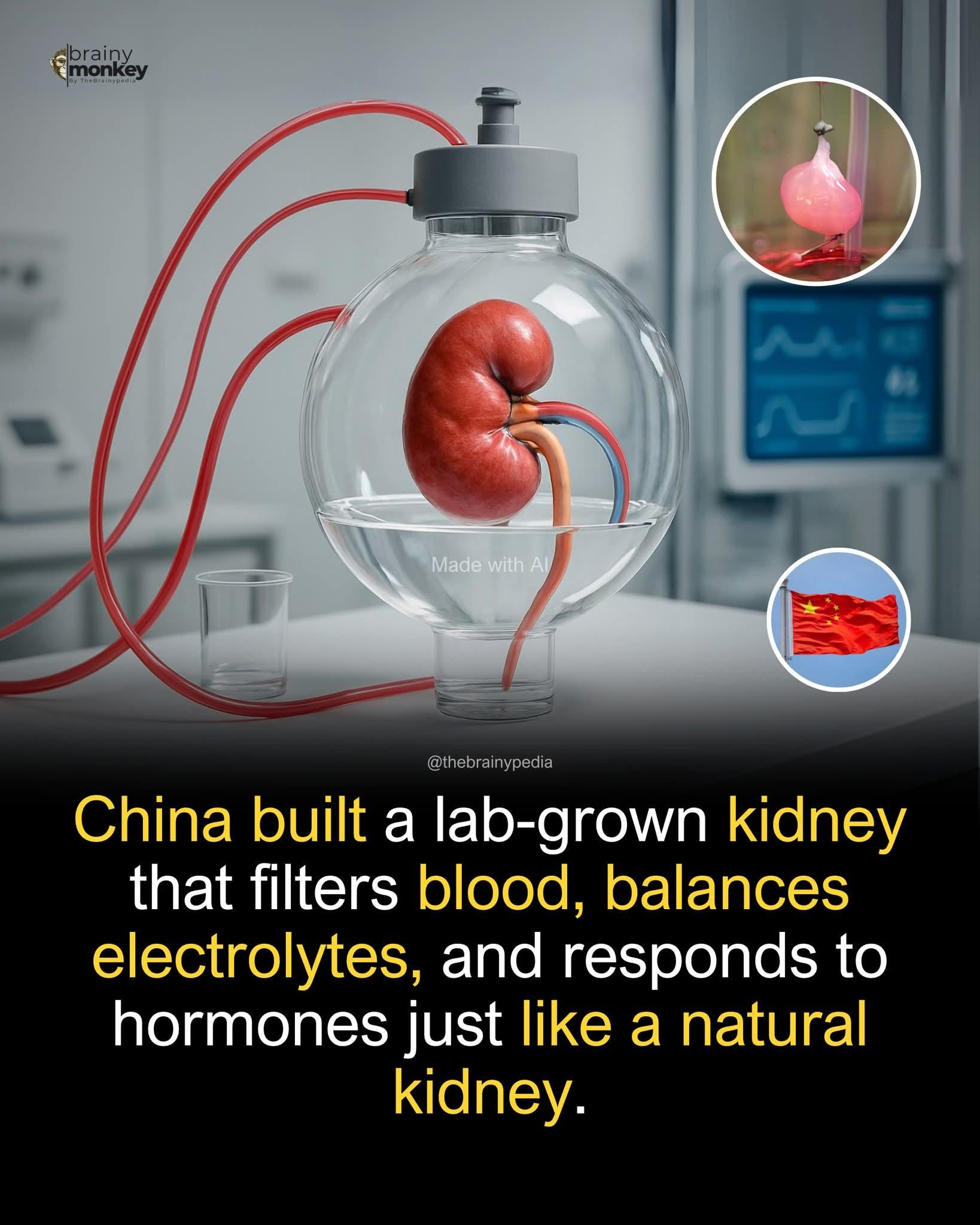
Chinese scientists have successfully grown a fully functional human kidney in a lab, marking a major breakthrough in regenerative medicine. According to Jungle Journalist, researchers in Shanghai used stem cell-derived organoids seeded onto a biodegradable hydrogel scaffold to create a kidney that mimics real biological function.
The lab-grown organ developed into a working nephron system, complete with glomeruli, tubules, and urine-collecting structures. Once connected to an artificial circulatory loop, the kidney began filtering blood plasma in real time, just like a natural kidney.
What makes this achievement especially remarkable is that the bioengineered kidney not only filtered blood and produced urine, but also balanced electrolytes and responded to hormonal signals such as ADH and aldosterone. These responses allowed it to adjust water retention and salt levels, demonstrating a level of physiological complexity rarely seen in lab-grown organs.
The kidney remained functional for over 60 hours in lab conditions, and the team is now conducting scaled trials on pigs, with human pilot studies expected within two years. Their ultimate goal is to create implant-ready kidneys using a patient’s own cells, eliminating the risk of transplant rejection.
This development could revolutionize treatment for kidney failure, which affects over 850 million people globally. If successful, it would mark a major step toward on-demand organ manufacturing, the holy grail of regenerative medicine.
The lab-grown organ developed into a working nephron system, complete with glomeruli, tubules, and urine-collecting structures. Once connected to an artificial circulatory loop, the kidney began filtering blood plasma in real time, just like a natural kidney.
What makes this achievement especially remarkable is that the bioengineered kidney not only filtered blood and produced urine, but also balanced electrolytes and responded to hormonal signals such as ADH and aldosterone. These responses allowed it to adjust water retention and salt levels, demonstrating a level of physiological complexity rarely seen in lab-grown organs.
The kidney remained functional for over 60 hours in lab conditions, and the team is now conducting scaled trials on pigs, with human pilot studies expected within two years. Their ultimate goal is to create implant-ready kidneys using a patient’s own cells, eliminating the risk of transplant rejection.
This development could revolutionize treatment for kidney failure, which affects over 850 million people globally. If successful, it would mark a major step toward on-demand organ manufacturing, the holy grail of regenerative medicine.
Chinese scientists have successfully grown a fully functional human kidney in a lab, marking a major breakthrough in regenerative medicine. According to Jungle Journalist, researchers in Shanghai used stem cell-derived organoids seeded onto a biodegradable hydrogel scaffold to create a kidney that mimics real biological function.
The lab-grown organ developed into a working nephron system, complete with glomeruli, tubules, and urine-collecting structures. Once connected to an artificial circulatory loop, the kidney began filtering blood plasma in real time, just like a natural kidney.
What makes this achievement especially remarkable is that the bioengineered kidney not only filtered blood and produced urine, but also balanced electrolytes and responded to hormonal signals such as ADH and aldosterone. These responses allowed it to adjust water retention and salt levels, demonstrating a level of physiological complexity rarely seen in lab-grown organs.
The kidney remained functional for over 60 hours in lab conditions, and the team is now conducting scaled trials on pigs, with human pilot studies expected within two years. Their ultimate goal is to create implant-ready kidneys using a patient’s own cells, eliminating the risk of transplant rejection.
This development could revolutionize treatment for kidney failure, which affects over 850 million people globally. If successful, it would mark a major step toward on-demand organ manufacturing, the holy grail of regenerative medicine.
0 Kommentare
0 Geteilt
839 Ansichten