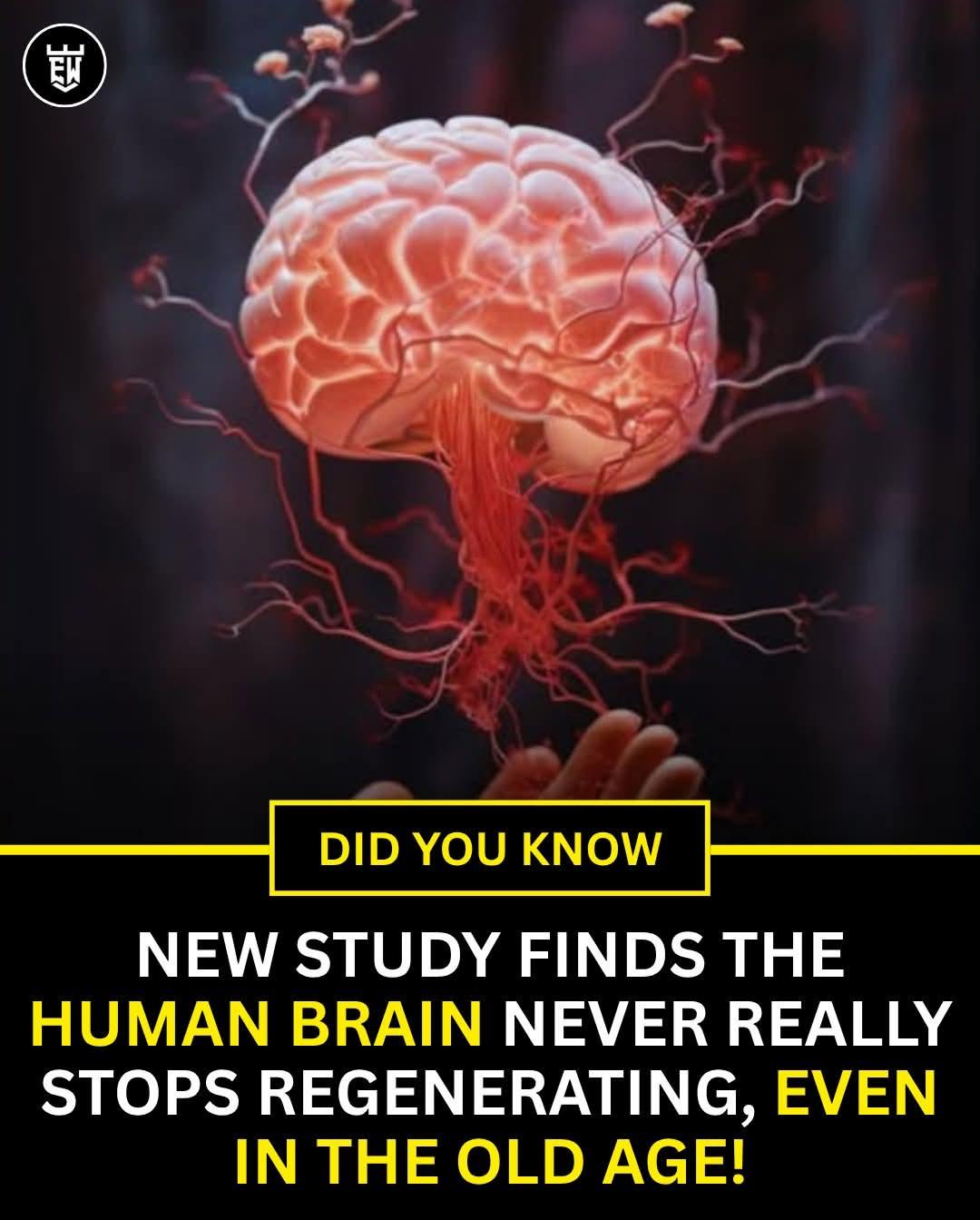
For years, scientists believed that once we reached adulthood, our brains stopped producing new neurons. But groundbreaking research from Sweden’s Karolinska Institutet is rewriting the story. Their study has confirmed that adult human brains continue to generate new neurons, even in people as old as 78 years. This discovery is a major breakthrough in neuroscience and offers renewed hope for treating memory loss and brain disorders.
Using cutting-edge tools like single-nucleus RNA sequencing, RNAscope, and spatial transcriptomics, researchers traced the formation of new neurons in the dentate gyrus, a crucial part of the hippocampus responsible for memory and learning. These tools allowed them to observe actively dividing neural progenitor cells, proving that neurogenesis, once thought to stop after childhood, is still occurring throughout adulthood.
This revelation not only changes our understanding of how the brain functions, but it also highlights how individual differences may affect cognitive aging. Some people naturally produce more new neurons than others, which could explain variations in learning, memory, and even vulnerability to brain diseases.
The findings open exciting new possibilities for regenerative medicine. By learning how to support or enhance this natural neurogenesis, scientists may develop therapies to slow or reverse the effects of Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, and other neurodegenerative diseases. It also brings new hope for mental health treatments, as the hippocampus plays a key role in mood regulation.
Your brain isn’t just surviving, it’s still growing, learning, and adapting, even well into old age.
Follow our page to stay updated on the most fascinating discoveries in science, health, and the power of the human mind.
#Neurogenesis #BrainHealth #Hippocampus #MindBlown #NeuroscienceNews #CognitiveScienceFor years, scientists believed that once we reached adulthood, our brains stopped producing new neurons. But groundbreaking research from Sweden’s Karolinska Institutet is rewriting the story. Their study has confirmed that adult human brains continue to generate new neurons, even in people as old as 78 years. This discovery is a major breakthrough in neuroscience and offers renewed hope for treating memory loss and brain disorders.
Using cutting-edge tools like single-nucleus RNA sequencing, RNAscope, and spatial transcriptomics, researchers traced the formation of new neurons in the dentate gyrus, a crucial part of the hippocampus responsible for memory and learning. These tools allowed them to observe actively dividing neural progenitor cells, proving that neurogenesis, once thought to stop after childhood, is still occurring throughout adulthood.
This revelation not only changes our understanding of how the brain functions, but it also highlights how individual differences may affect cognitive aging. Some people naturally produce more new neurons than others, which could explain variations in learning, memory, and even vulnerability to brain diseases.
The findings open exciting new possibilities for regenerative medicine. By learning how to support or enhance this natural neurogenesis, scientists may develop therapies to slow or reverse the effects of Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, and other neurodegenerative diseases. It also brings new hope for mental health treatments, as the hippocampus plays a key role in mood regulation.
Your brain isn’t just surviving, it’s still growing, learning, and adapting, even well into old age.
Follow our page to stay updated on the most fascinating discoveries in science, health, and the power of the human mind.
#Neurogenesis #BrainHealth #Hippocampus #MindBlown #NeuroscienceNews #CognitiveScience