The Universe Comes Into Focus: Vera Rubin Telescope Reveals Millions of Hidden Galaxies in First Images
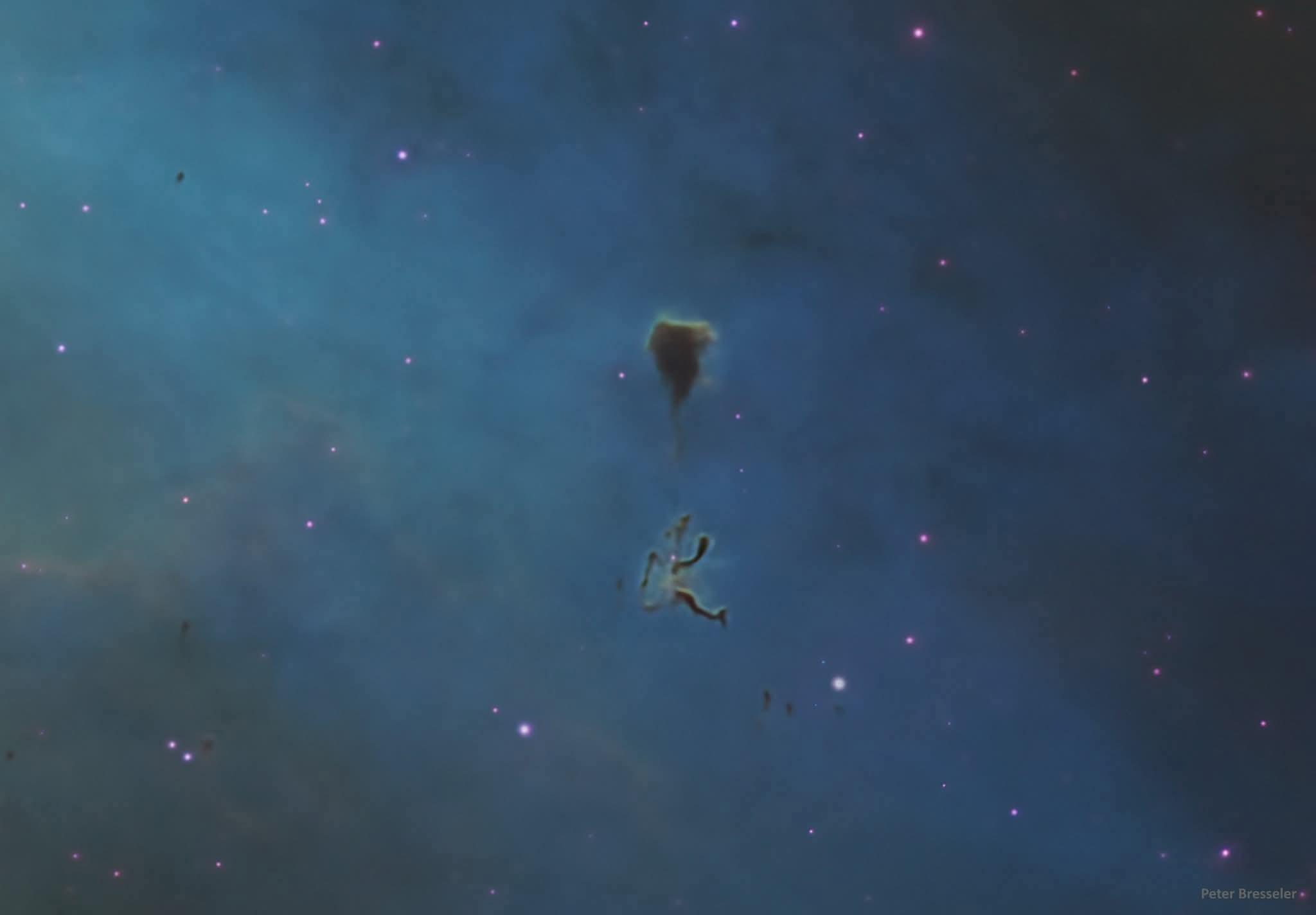
In a breathtaking debut, the Vera C. Rubin Observatory the largest astronomical survey telescope ever constructed has delivered its first full-sky images, and they are nothing short of extraordinary. Capturing a dazzling expanse of deep space in unprecedented detail, the observatory’s initial snapshots unveiled millions of previously unseen galaxies, stretching the boundaries of what we know about the cosmos. From spiral galaxies in mid-rotation to faint, ghostly clusters glowing on the edge of visibility, the images open a new window into the large-scale structure of the universe.
What makes the Vera Rubin Telescope unique is its 8.4-meter mirror and revolutionary 3.2-gigapixel camera the most powerful digital camera ever built for astronomy. Its mission is bold: map the southern sky every few nights for ten years, creating a dynamic, time-lapse survey of the changing night sky. With this capability, scientists expect to uncover everything from near-Earth asteroids and supernovae to signs of dark matter and the subtle movements of stars. This first image teeming with bright points of light and dramatic galactic interactions—represents only a sliver of what’s to come.
These first observations aren’t just beautiful they’re transformative. The data will serve as a cosmic census, helping astronomers chart the universe's history and better understand the invisible forces shaping its future. The Vera Rubin Observatory stands not only as a tribute to its pioneering namesake but as a game-changer in our quest to comprehend the universe’s deepest mysteries.
What makes the Vera Rubin Telescope unique is its 8.4-meter mirror and revolutionary 3.2-gigapixel camera—the most powerful digital camera ever built for astronomy. Its mission is bold: map the southern sky every few nights for ten years, creating a dynamic, time-lapse survey of the changing night sky. With this capability, scientists expect to uncover everything from near-Earth asteroids and supernovae to signs of dark matter and the subtle movements of stars. This first image teeming with bright points of light and dramatic galactic interactions—represents only a sliver of what’s to come.
#RubinObservatory #verarubintelescope #spacephotography #spaceexplorationThe Universe Comes Into Focus: Vera Rubin Telescope Reveals Millions of Hidden Galaxies in First Images
In a breathtaking debut, the Vera C. Rubin Observatory the largest astronomical survey telescope ever constructed has delivered its first full-sky images, and they are nothing short of extraordinary. Capturing a dazzling expanse of deep space in unprecedented detail, the observatory’s initial snapshots unveiled millions of previously unseen galaxies, stretching the boundaries of what we know about the cosmos. From spiral galaxies in mid-rotation to faint, ghostly clusters glowing on the edge of visibility, the images open a new window into the large-scale structure of the universe.
What makes the Vera Rubin Telescope unique is its 8.4-meter mirror and revolutionary 3.2-gigapixel camera the most powerful digital camera ever built for astronomy. Its mission is bold: map the southern sky every few nights for ten years, creating a dynamic, time-lapse survey of the changing night sky. With this capability, scientists expect to uncover everything from near-Earth asteroids and supernovae to signs of dark matter and the subtle movements of stars. This first image teeming with bright points of light and dramatic galactic interactions—represents only a sliver of what’s to come.
These first observations aren’t just beautiful they’re transformative. The data will serve as a cosmic census, helping astronomers chart the universe's history and better understand the invisible forces shaping its future. The Vera Rubin Observatory stands not only as a tribute to its pioneering namesake but as a game-changer in our quest to comprehend the universe’s deepest mysteries.
What makes the Vera Rubin Telescope unique is its 8.4-meter mirror and revolutionary 3.2-gigapixel camera—the most powerful digital camera ever built for astronomy. Its mission is bold: map the southern sky every few nights for ten years, creating a dynamic, time-lapse survey of the changing night sky. With this capability, scientists expect to uncover everything from near-Earth asteroids and supernovae to signs of dark matter and the subtle movements of stars. This first image teeming with bright points of light and dramatic galactic interactions—represents only a sliver of what’s to come.
#RubinObservatory #verarubintelescope #spacephotography #spaceexploration