The Future of Energy: Unlocking the Power of Nuclear Fusion Through Cutting-Edge Research

Introduction
Nuclear fusion, often hailed as the "holy grail" of energy production, promises a future of virtually limitless, clean, and safe power. Unlike nuclear fission, which splits heavy atoms and produces long-lived radioactive waste, fusion merges light atomic nuclei—such as hydrogen isotopes—to release enormous amounts of energy, mimicking the processes powering our sun. As global energy demands rise and climate change concerns intensify, research into nuclear fusion has accelerated, bringing us closer than ever to realizing this revolutionary energy source.

What is Nuclear Fusion?
At its core, nuclear fusion involves combining two light atomic nuclei to form a heavier nucleus, releasing energy in the process. The most common fusion reactions under study involve isotopes of hydrogen, deuterium, and tritium. When these nuclei fuse, they release energy many times greater than chemical reactions like burning fossil fuels, without the harmful greenhouse gas emissions.
Why Nuclear Fusion Matters
Clean Energy: Fusion produces no carbon dioxide or other greenhouse gases, making it an environmentally friendly alternative to fossil fuels.
Abundant Fuel Supply: Deuterium can be extracted from seawater, and lithium (used to breed tritium) is plentiful, ensuring a virtually inexhaustible fuel supply.
Safety: Fusion reactions are inherently safe; they require precise conditions to sustain, and any disruption causes the reaction to stop immediately, eliminating meltdown risks.
Minimal Waste: Fusion produces far less radioactive waste than fission, and the waste it does produce has a much shorter half-life.
Recent Advances in Nuclear Fusion Research
The journey to practical fusion power has been challenging, but recent breakthroughs have sparked optimism:
ITER Project: The International Thermonuclear Experimental Reactor (ITER) in France is the world’s largest fusion experiment, aiming to demonstrate net energy gain from fusion by the late 2020s.
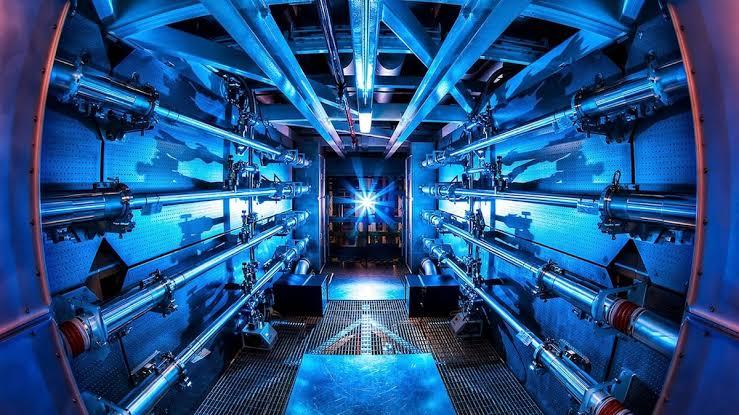
National Ignition Facility (NIF): In the USA, NIF has achieved significant milestones in inertial confinement fusion, using powerful lasers to initiate fusion reactions.
Private Sector Innovations: Companies like Commonwealth Fusion Systems and Tokamak Energy are developing compact, high-field magnets and advanced tokamak designs to accelerate commercialization.
Artificial Intelligence: AI and machine learning are being used to optimize plasma control and predict instabilities, improving reactor efficiency.
Challenges Ahead
Despite progress, several technical hurdles remain:
Sustaining Plasma: Fusion requires maintaining plasma at extremely high temperatures (over 100 million °C) for a sustained period.
Materials Durability: Reactor components must withstand intense neutron bombardment and heat flux.
Cost and Scale: Building and operating fusion reactors is capital-intensive, requiring continued investment and international collaboration.
The Road to Commercial Fusion Power
Experts predict that commercial fusion power plants could become a reality by the 2040s or 2050s. Continued research, innovation, and funding are critical to overcoming remaining obstacles. Governments and private entities worldwide are increasingly recognizing fusion's potential to transform the global energy landscape.
Conclusion
Nuclear fusion stands at the forefront of a clean energy revolution, offering hope for a sustainable future free from fossil fuel dependence. With ongoing research pushing the boundaries of science and technology, the dream of harnessing the power of the stars here on Earth is closer than ever. Staying informed and supporting fusion research can help accelerate this exciting journey toward a brighter, greener tomorrow.
- nuclear_fusion
- fusion_energy
- clean_energy
- ITER
- National_Ignition_Facility
- fusion_research
- sustainable_energy
- renewable_energy
- fusion_power
- plasma_physics
- energy_innovation
- climate_change_solutions
- fusion_reactor
- energy_future
- tokamak
- AI_in_fusion
- fusion_technology
- energy_breakthroughs
- green_energy
- fusion_fuel