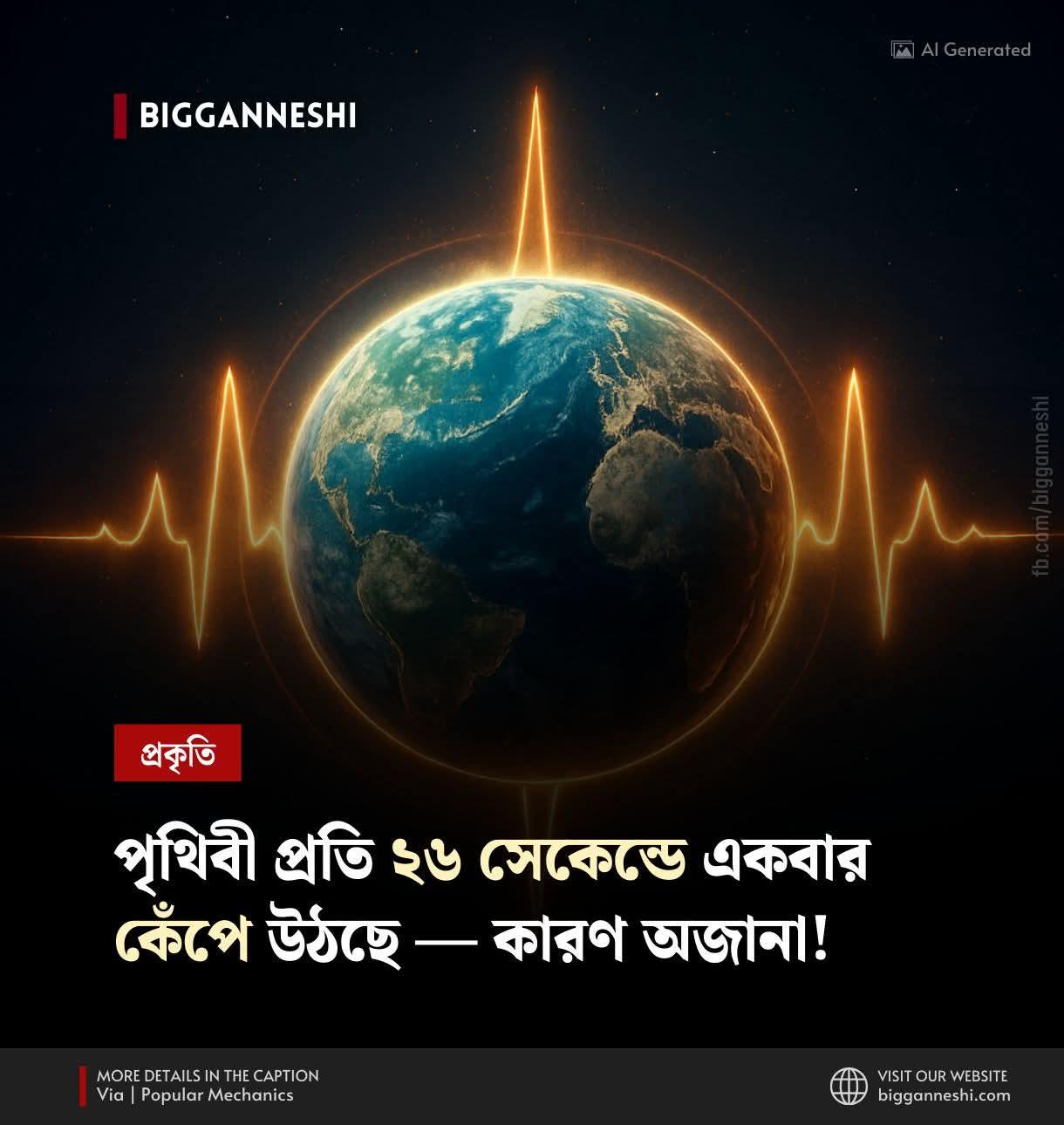
পৃথিবী প্রতি ২৬ সেকেন্ডে একবার করে কেঁপে উঠছে! এই কম্পন এতটাই মৃদু যে আমরা টের পাই না, কিন্তু সিসমোমিটার (ভূমিকম্প মাপার যন্ত্র) এটা বুঝতে পারে। এটি আবিস্কারের ৬৫ বছরের মধ্যে নানা গবেষণা হলেও এখনো পর্যন্ত বিজ্ঞানীরা নিশ্চিতভাবে বলতে পারেননি পৃথিবী কেন এমনভাবে বারবার কেঁপে ওঠে।
এই কম্পন প্রথম শনাক্ত করেন বিজ্ঞানী জ্যাক অলিভার। তিনি দেখেন, এটি আসছে আটলান্টিক মহাসাগর থেকে, বিশেষ করে গ্রীষ্মকালে এর তীব্রতা বেড়ে যায়। পরে ১৯৮০ সালে ভূতত্ত্ববিদ গ্যারি হোলকম্ব আবিষ্কার করেন, ঝড়ের সময় এই কম্পন সবচেয়ে শক্তিশালী হয়।
দীর্ঘদিন পর ২০০৫ সালে কলোরাডো বিশ্ববিদ্যালয়ের গবেষকরা আবারও এটি শনাক্ত করেন এবং উৎস নির্ধারণ করেন আফ্রিকার পশ্চিম উপকূলের গিনি উপসাগরে। ঠিক কী কারণে এটি হচ্ছে, তা নিশ্চিত হতে পারেননি তারা।
২০১১ সালে ওয়াশিংটন ইউনিভার্সিটির গবেষক গ্যারেট ইউলার আরও নির্দিষ্টভাবে দেখান, এর উৎস গিনি উপসাগরের "বাইট অব বনি" এলাকা। তার মতে, সমুদ্রের ঢেউ যখন মহাদেশীয় প্রান্তে আঘাত করে, তখন সমুদ্রতল কেঁপে ওঠার কারণে এই কম্পন হয়। তবে চীনের কিছু বিজ্ঞানীর মতে, এর পেছনে কারণ হতে পারে কাছের সাও টোমে (Sao Tome) দ্বীপের সক্রিয় আগ্নেয়গিরি। জাপানের আসো (Aso) আগ্নেয়গিরি থেকেও একই ধরনের কম্পন পাওয়া গেছে।
তবুও প্রশ্ন রয়েই গেছে, বিশ্বে আরও অনেক মহাদেশীয় প্রান্ত ও আগ্নেয়গিরি থাকলেও এমন স্পন্দন সেখান থেকে আসে না। শুধু এই বিশেষ জায়গাতেই কেনো? প্রায় ৬০ বছর পেরিয়ে গেলেও এর আসল কারণ অজানা, যা ভবিষ্যতের বিজ্ঞানীদের জন্য কৌতূহল ও অনুসন্ধানের বড় এক চ্যালেঞ্জ হয়ে দাড়িয়েছে।
তাসিনুল সাকিফ
লেখক, বিজ্ঞান্বেষী
সূত্র : পপুলার মেকানিকস
#EarthScience #Geology #SeismicMystery #26SecondPulse #ScienceUnsolved #গবেষণা
এই কম্পন প্রথম শনাক্ত করেন বিজ্ঞানী জ্যাক অলিভার। তিনি দেখেন, এটি আসছে আটলান্টিক মহাসাগর থেকে, বিশেষ করে গ্রীষ্মকালে এর তীব্রতা বেড়ে যায়। পরে ১৯৮০ সালে ভূতত্ত্ববিদ গ্যারি হোলকম্ব আবিষ্কার করেন, ঝড়ের সময় এই কম্পন সবচেয়ে শক্তিশালী হয়।
দীর্ঘদিন পর ২০০৫ সালে কলোরাডো বিশ্ববিদ্যালয়ের গবেষকরা আবারও এটি শনাক্ত করেন এবং উৎস নির্ধারণ করেন আফ্রিকার পশ্চিম উপকূলের গিনি উপসাগরে। ঠিক কী কারণে এটি হচ্ছে, তা নিশ্চিত হতে পারেননি তারা।
২০১১ সালে ওয়াশিংটন ইউনিভার্সিটির গবেষক গ্যারেট ইউলার আরও নির্দিষ্টভাবে দেখান, এর উৎস গিনি উপসাগরের "বাইট অব বনি" এলাকা। তার মতে, সমুদ্রের ঢেউ যখন মহাদেশীয় প্রান্তে আঘাত করে, তখন সমুদ্রতল কেঁপে ওঠার কারণে এই কম্পন হয়। তবে চীনের কিছু বিজ্ঞানীর মতে, এর পেছনে কারণ হতে পারে কাছের সাও টোমে (Sao Tome) দ্বীপের সক্রিয় আগ্নেয়গিরি। জাপানের আসো (Aso) আগ্নেয়গিরি থেকেও একই ধরনের কম্পন পাওয়া গেছে।
তবুও প্রশ্ন রয়েই গেছে, বিশ্বে আরও অনেক মহাদেশীয় প্রান্ত ও আগ্নেয়গিরি থাকলেও এমন স্পন্দন সেখান থেকে আসে না। শুধু এই বিশেষ জায়গাতেই কেনো? প্রায় ৬০ বছর পেরিয়ে গেলেও এর আসল কারণ অজানা, যা ভবিষ্যতের বিজ্ঞানীদের জন্য কৌতূহল ও অনুসন্ধানের বড় এক চ্যালেঞ্জ হয়ে দাড়িয়েছে।
তাসিনুল সাকিফ
লেখক, বিজ্ঞান্বেষী
সূত্র : পপুলার মেকানিকস
#EarthScience #Geology #SeismicMystery #26SecondPulse #ScienceUnsolved #গবেষণা
পৃথিবী প্রতি ২৬ সেকেন্ডে একবার করে কেঁপে উঠছে! এই কম্পন এতটাই মৃদু যে আমরা টের পাই না, কিন্তু সিসমোমিটার (ভূমিকম্প মাপার যন্ত্র) এটা বুঝতে পারে। এটি আবিস্কারের ৬৫ বছরের মধ্যে নানা গবেষণা হলেও এখনো পর্যন্ত বিজ্ঞানীরা নিশ্চিতভাবে বলতে পারেননি পৃথিবী কেন এমনভাবে বারবার কেঁপে ওঠে।
এই কম্পন প্রথম শনাক্ত করেন বিজ্ঞানী জ্যাক অলিভার। তিনি দেখেন, এটি আসছে আটলান্টিক মহাসাগর থেকে, বিশেষ করে গ্রীষ্মকালে এর তীব্রতা বেড়ে যায়। পরে ১৯৮০ সালে ভূতত্ত্ববিদ গ্যারি হোলকম্ব আবিষ্কার করেন, ঝড়ের সময় এই কম্পন সবচেয়ে শক্তিশালী হয়।
দীর্ঘদিন পর ২০০৫ সালে কলোরাডো বিশ্ববিদ্যালয়ের গবেষকরা আবারও এটি শনাক্ত করেন এবং উৎস নির্ধারণ করেন আফ্রিকার পশ্চিম উপকূলের গিনি উপসাগরে। ঠিক কী কারণে এটি হচ্ছে, তা নিশ্চিত হতে পারেননি তারা।
২০১১ সালে ওয়াশিংটন ইউনিভার্সিটির গবেষক গ্যারেট ইউলার আরও নির্দিষ্টভাবে দেখান, এর উৎস গিনি উপসাগরের "বাইট অব বনি" এলাকা। তার মতে, সমুদ্রের ঢেউ যখন মহাদেশীয় প্রান্তে আঘাত করে, তখন সমুদ্রতল কেঁপে ওঠার কারণে এই কম্পন হয়। তবে চীনের কিছু বিজ্ঞানীর মতে, এর পেছনে কারণ হতে পারে কাছের সাও টোমে (Sao Tome) দ্বীপের সক্রিয় আগ্নেয়গিরি। জাপানের আসো (Aso) আগ্নেয়গিরি থেকেও একই ধরনের কম্পন পাওয়া গেছে।
তবুও প্রশ্ন রয়েই গেছে, বিশ্বে আরও অনেক মহাদেশীয় প্রান্ত ও আগ্নেয়গিরি থাকলেও এমন স্পন্দন সেখান থেকে আসে না। শুধু এই বিশেষ জায়গাতেই কেনো? প্রায় ৬০ বছর পেরিয়ে গেলেও এর আসল কারণ অজানা, যা ভবিষ্যতের বিজ্ঞানীদের জন্য কৌতূহল ও অনুসন্ধানের বড় এক চ্যালেঞ্জ হয়ে দাড়িয়েছে।
তাসিনুল সাকিফ
লেখক, বিজ্ঞান্বেষী
সূত্র : পপুলার মেকানিকস
#EarthScience #Geology #SeismicMystery #26SecondPulse #ScienceUnsolved #গবেষণা
0 Comments
0 Shares
4K Views