The Milky Way Is Racing Through Space at 2 Million km/h and We’re All Along for the Ride
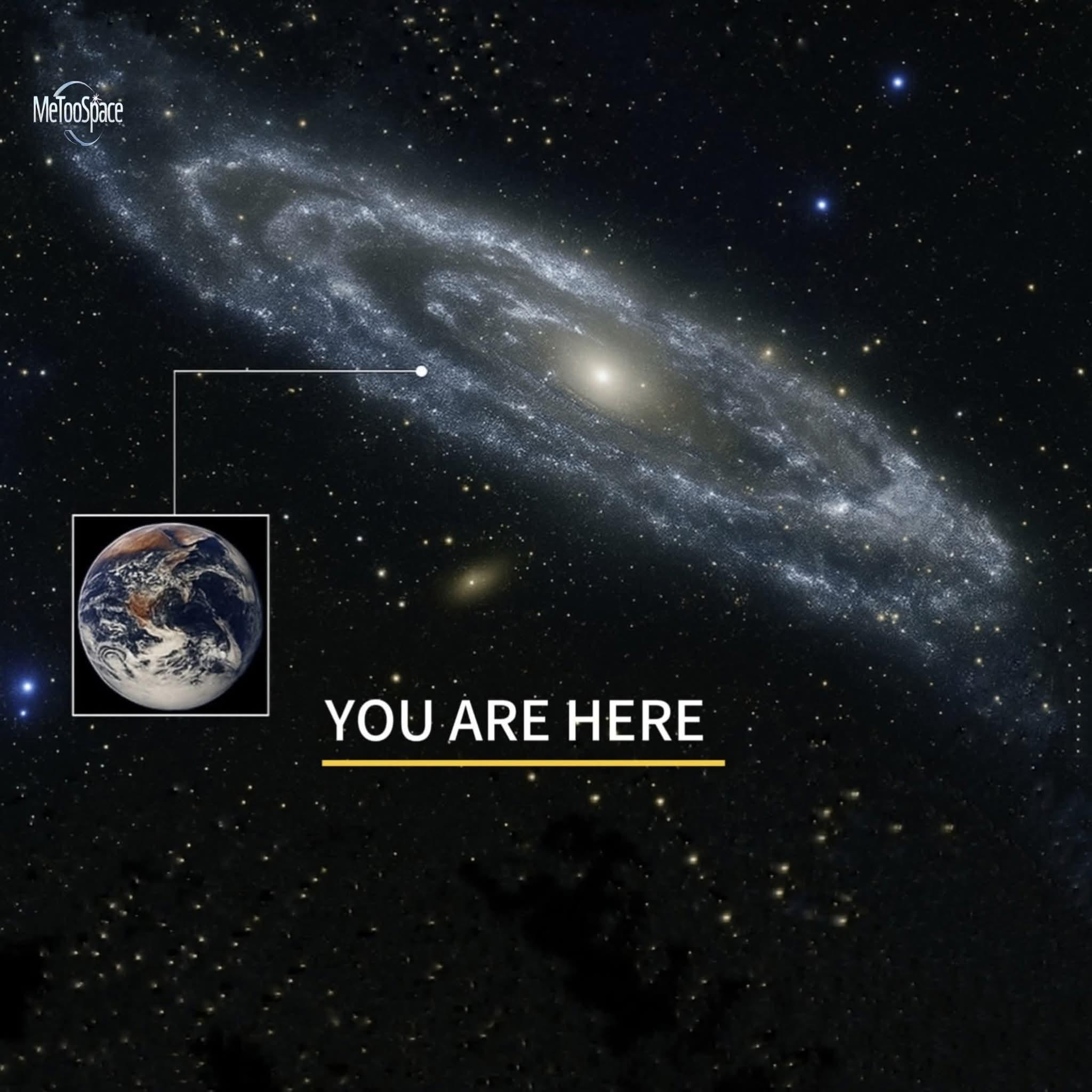
Our home galaxy, the Milky Way, isn’t quietly floating through the cosmos it’s speeding across space at a mind-blowing 2 million kilometers per hour (about 1.24 million mph). This galactic momentum isn’t random. It’s fueled by gravitational giants like the Shapley Supercluster, an enormous concentration of galaxies located roughly 650 million light-years away. The immense mass of these far-off structures exerts a powerful gravitational pull, drawing not just the Milky Way, but countless galaxies along with it like leaves caught in a cosmic current.
But the story doesn’t stop there. The Milky Way belongs to the Local Group, a collection of nearby galaxies, which is itself being tugged toward another mysterious region called the Great Attractor a gravitational anomaly we’re still working to fully understand. All of this movement exists within a vast hierarchy of motions: Earth spins on its axis, orbits the Sun, the Sun orbits the Milky Way’s center, and the entire galaxy is being hurled across space in this grand, layered flow of cosmic motion.
Though we don’t feel it, scientists can actually measure our galaxy’s incredible speed using subtle shifts in the cosmic microwave background radiation—the relic glow left behind from the Big Bang. In the direction we're moving, this radiation appears slightly warmer; in the opposite direction, slightly cooler. It’s a silent yet powerful indicator that we’re not stationary beings in the universe—we're passengers in a galaxy-sized spaceship, rocketing through space in a gravitational dance shaped by colossal forces billions of light-years away.
Credit: Motion estimates derived from NASA, ESA, and Planck satellite observations; gravitational insights supported by research on the Shapley Supercluster and Great Attractor (Astrophysical Journal, 2025).
The Milky Way Is Racing Through Space at 2 Million km/h and We’re All Along for the Ride
Our home galaxy, the Milky Way, isn’t quietly floating through the cosmos it’s speeding across space at a mind-blowing 2 million kilometers per hour (about 1.24 million mph). This galactic momentum isn’t random. It’s fueled by gravitational giants like the Shapley Supercluster, an enormous concentration of galaxies located roughly 650 million light-years away. The immense mass of these far-off structures exerts a powerful gravitational pull, drawing not just the Milky Way, but countless galaxies along with it like leaves caught in a cosmic current.
But the story doesn’t stop there. The Milky Way belongs to the Local Group, a collection of nearby galaxies, which is itself being tugged toward another mysterious region called the Great Attractor a gravitational anomaly we’re still working to fully understand. All of this movement exists within a vast hierarchy of motions: Earth spins on its axis, orbits the Sun, the Sun orbits the Milky Way’s center, and the entire galaxy is being hurled across space in this grand, layered flow of cosmic motion.
Though we don’t feel it, scientists can actually measure our galaxy’s incredible speed using subtle shifts in the cosmic microwave background radiation—the relic glow left behind from the Big Bang. In the direction we're moving, this radiation appears slightly warmer; in the opposite direction, slightly cooler. It’s a silent yet powerful indicator that we’re not stationary beings in the universe—we're passengers in a galaxy-sized spaceship, rocketing through space in a gravitational dance shaped by colossal forces billions of light-years away.
Credit: Motion estimates derived from NASA, ESA, and Planck satellite observations; gravitational insights supported by research on the Shapley Supercluster and Great Attractor (Astrophysical Journal, 2025).