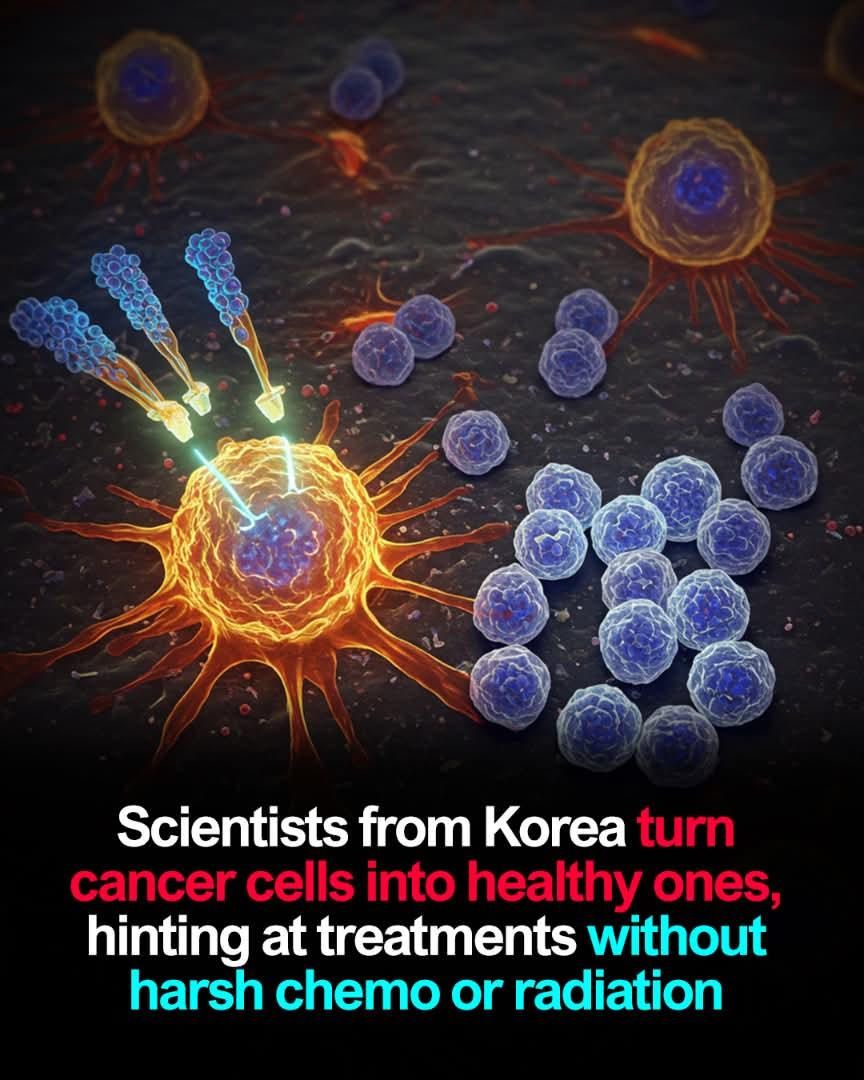
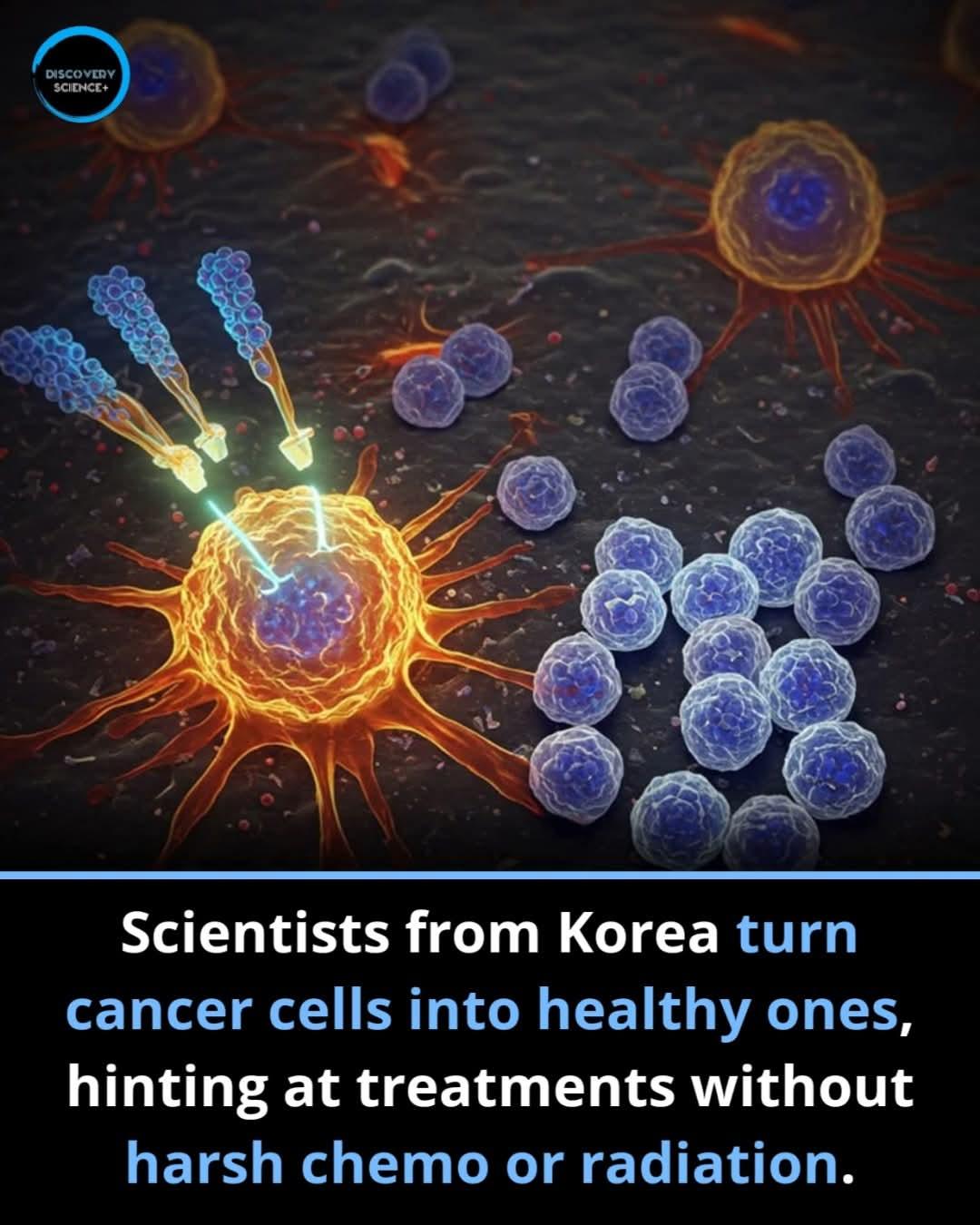
In a groundbreaking development, researchers in South Korea are rewriting the rules of cancer treatment—not by destroying tumors, but by transforming them back into healthy cells.
Instead of radiation or chemotherapy, this method reprograms the internal environment and genetic behavior of cancer cells, effectively reversing their malignant traits. The goal? To restore normal function, not eradicate what's inside.
Though still in the early experimental phase, the implications are profound:
Kind of compassion therapy: a gentler path forward
Targeted precision without widespread damage
Potential breakthrough for aggressive, treatment-resistant cancers
Imagine a future where cancer treatment isn’t about annihilation, but restoration—turning back time at a cellular level.
Instead of radiation or chemotherapy, this method reprograms the internal environment and genetic behavior of cancer cells, effectively reversing their malignant traits. The goal? To restore normal function, not eradicate what's inside.
Though still in the early experimental phase, the implications are profound:
Kind of compassion therapy: a gentler path forward
Targeted precision without widespread damage
Potential breakthrough for aggressive, treatment-resistant cancers
Imagine a future where cancer treatment isn’t about annihilation, but restoration—turning back time at a cellular level.
In a groundbreaking development, researchers in South Korea are rewriting the rules of cancer treatment—not by destroying tumors, but by transforming them back into healthy cells.
Instead of radiation or chemotherapy, this method reprograms the internal environment and genetic behavior of cancer cells, effectively reversing their malignant traits. The goal? To restore normal function, not eradicate what's inside.
Though still in the early experimental phase, the implications are profound:
Kind of compassion therapy: a gentler path forward
Targeted precision without widespread damage
Potential breakthrough for aggressive, treatment-resistant cancers
Imagine a future where cancer treatment isn’t about annihilation, but restoration—turning back time at a cellular level.
0 Commentaires
0 Parts
624 Vue